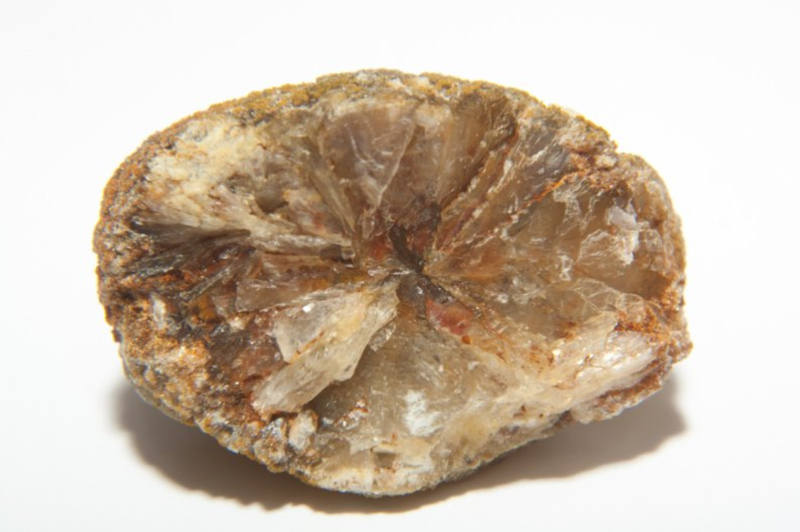
Gallstones are small stones or lumps, which form in the gallbladder, a small pear-shaped organ located under the liver. The stones form when there is a chemical imbalance inside the gallbladder. People who are overweight or obese are more likely to develop gallstones. There are two main types of gallstones:
- Cholesterol stones are the most common kind, making 80% of gallstones. They are usually yellow-green in color.
- Pigment stones are smaller and darker than cholesterol stones, usually dark brown or black in color. They are made of chemicals that exist in the gallstones, known as bilirubin, which is a fluid your liver makes.

The cause of gallstones is still unclear, but doctors think that gallstones may form when your gallbladder does not empty correctly, your bile contains too much cholesterol, or your bile contains too much bilirubin. You are more likely to develop gallstones if you are:
- Obese. Obesity can raise the cholesterol level and make it hard for your gallbladder to empty correctly.
- Female. Especially if you take birth control pills, hormone replacement therapy for menopause symptoms, are pregnant or have had children. The extra estrogen in your body can increase cholesterol and make it harder for the gallbladder to empty correctly.
- Suffering from diabetes. People with diabetes have a tendency to have higher levels of triglycerides, which is a type of blood fat that is a risk factor for gallstones.
- 40 years of age or older. The risk of gallstones increases as you get older.
- Taking medicine to lower your cholesterol. Some of the medicine can boost cholesterol in bile and increase your risk of getting cholesterol stones.
- Fasting. Your gallbladder does not get as much use when you are fasting.
- A certain ethnic group. Gallstones have a high chance of occurring if they run in your family, and they are more likely to happen among some ethnic groups, such as Native Americans and Mexican-Americans.
In many cases, these stones do not cause any symptoms and do not need to be treated because the stones stay in the gallbladder and cause no problems. However, if a gallstone is blocking a bile duct inside the gallbladder, it can trigger an intense abdominal pain (biliary colic). When this happens, you will feel some symptoms including sudden intensifying pain in the upper right portion of the abdomen and the center of the abdomen, back pain, nausea, and pain in the right shoulder. The pain normally lasts between one to five hours and will need to be treated right away. Sometimes, gallstones can lead to cholecystitis or inflammation of the gallbladder. This condition can cause persistent pain, a fever, and jaundice. When gallstones cause complications, it is known as gallstone disease or cholelithiasis.
Very severe cases of gallstone can be life-threatening, especially for people who are already in poor health. Other than cholecystitis, complications of gallstones may include blockage of the common bile duct, blockage of the pancreatic duct, and gallbladder cancer.
Many cases of gallstones are discovered by accident, usually when an individual is being treated for a different condition. When your doctor suspects gallstones, you will have to undergo a physical exam, including blood tests, ultrasound, CT scan, MRCP, HIDA scan, Endoscopic ultrasound, and ERCP. Gallstone disease is easily treated with surgery to take out the gallbladder. There are two types of operations:
- Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is the most common procedure. During this surgery, the surgeon makes small incisions in the belly and passes instruments, a light, and a camera through the cuts. You can go home the same day of the surgery.
- Open cholecystectomy is an operation where the surgeon will make a larger cut in the belly to remove your gallbladder, and you will need to stay in the hospital for a few days.
There are some alternatives to treating gallstones if you do not want to undergo a surgery or if you have a medical condition where your doctor feels you should not have an operation. Your doctor may prescribe Chenodol, ursodiol (Actigall, Urso 250, Urso Forte), or both. The drugs dissolve cholesterol stones, but mild diarrhea can be a side effect. However, if you choose to use medication, it may take years for them to completely dissolve the stones and the stones may come back after you stop taking the medications.
It is always better to prevent gallstones from developing instead of treating it. Although some factors such as age, ethnic origin, and sex cannot be altered, it is possible to reduce the risk by following a healthy lifestyle. Try to stick to your usual mealtimes every day because skipping meals or fasting can increase your risk of developing gallstones. You should also maintain a healthy weight by reducing the calories you eat and increasing your physical activity. However, if you need to lose weight, you will need to lose it gradually as rapid weight loss is a big risk factor for gallstones.